:)
슬라이딩 윈도우 기반 차선 인식 본문
슬라이딩 윈도우 기반의 차선인식 과정
- Image Read : 카메라 영상신호를 이미지로 읽기
- Warping : 원근변환으로 이미지 변형
- Gaussian Blur : 노이즈 제거
- Threshold : 이진 이미지로 변환
- Histogram : 히스토그램에서 차선 위치 추출
- Sliding Window : 슬라이딩 윈도우 좌우에 9개씩 쌓기
- Polyfit : 2차 함수 그래프로 차선 그리기
- 차선 영역 표시 : 원본 이미지에 차선 영역 오버레이
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import numpy as np
import cv2, random, math, copy
Width = 640
Height = 480
cap = cv2.VideoCapture("xycar_track1.mp4")
window_title = 'camera'
warp_img_w = 320
warp_img_h = 240
warpx_margin = 20
warpy_margin = 3
nwindows = 9 # 슬라이딩 윈도우 개수
margin = 12 # 슬라이딩 윈도우 넓이
minpix = 5 # 선을 그리기 위해 최소한 있어야 할 점의 개수
lane_bin_th = 145
warp_src = np.array([
[230-warpx_margin, 300-warpy_margin],
[45-warpx_margin, 450+warpy_margin],
[445+warpx_margin, 300-warpy_margin],
[610+warpx_margin, 450+warpy_margin]
], dtype=np.float32)
warp_dist = np.array([
[0,0],
[0,warp_img_h],
[warp_img_w,0],
[warp_img_w, warp_img_h]
], dtype=np.float32)
calibrated = True
if calibrated:
# 자이카 카메라로 촬영한 동영상, Calibration 보정값을 사용
mtx = np.array([
[422.037858, 0.0, 245.895397],
[0.0, 435.589734, 163.625535],
[0.0, 0.0, 1.0]
])
dist = np.array([-0.289296, 0.061035, 0.001786, 0.015238, 0.0])
cal_mtx, cal_roi = cv2.getOptimalNewCameraMatrix(mtx, dist, (Width, Height), 1, (Width, Height))
def calibrate_image(frame):
global Width, Height
global mtx, dist
global cal_mtx, cal_roi
#보정 행렬값을 적용하여 이미지를 반듯하게 수정하는 함수
tf_image = cv2.undistort(frame, mtx, dist, None, cal_mtx)
x, y, w, h = cal_roi
tf_image = tf_image[y:y+h, x:x+w]
return cv2.resize(tf_image, (Width, Height))
# 변환전과 후의 4개 점 좌표를 전달해서 이미지를 원근변환 처리하여 새로운 이미지로 만든다
def warp_image(img, src, dst, size):
M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(src, dst)
Minv = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(dst, src)
warp_img = cv2.warpPerspective(img, M, size, flags=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
return warp_img, M, Minv
def warp_process_image(img):
global nwindows
global margin
global minpix
global lane_bin_th
blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(img,(5, 5), 0) # 노이즈 제거
# HLS 포맷에서 L채널을 이요하여 흰색선을 쉽게 구분
_, L, _ = cv2.split(cv2.cvtColor(blur, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HLS))
# L채널 이미지의 분할부를 확실하게 만들기 위해 바이너리
_, lane = cv2.threshold(L, lane_bin_th, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
histogram = np.sum(lane[lane.shape[0]//2:,:], axis=0)
# x축을 반으로 나누어 왼쪽 차선과 오른쪽 차선을 구분
midpoint = np.int(histogram.shape[0]/2)
# 왼쪽 절반 구역에서 흰색 픽셀의 개수가 가장 많은 위치를 슬라이딩 윈도우의 왼쪽 시작 위치로 잡는다.
leftx_current = np.argmax(histogram[:midpoint])
# 오른쪽 절반 구역에서 흰색 픽셀의 개수가 가장 많은 위치를 슬라이딩 윈도우의 오른쪽 시작 위치로 잡는다.
rightx_current = np.argmax(histogram[midpoint:]) + midpoint
window_height = np.int(lane.shape[0]/nwindows) #240/9 = 26.XX
nz = lane.nonzero()
left_lane_inds = []
right_lane_inds = []
lx, ly, rx, ry = [], [], [], []
out_img = np.dstack((lane, lane, lane))*255
for window in range(nwindows):
win_yl = lane.shape[0] - (window+1)*window_height
win_yh = lane.shape[0] - window*window_height
win_xll = leftx_current - margin # 녹색사각형 크기 : 가로 24, 세로 26
win_xlh = leftx_current + margin
win_xrl = rightx_current - margin
win_xrh = rightx_current + margin
cv2.rectangle(out_img,(win_xll,win_yl),(win_xlh,win_yh),(0,255,0), 2)
cv2.rectangle(out_img,(win_xrl,win_yl),(win_xrh,win_yh),(0,255,0), 2)
# 슬라이딩 윈도우 박스(녹색박스) 하나 안에 있는 흰색 픽셀의 x좌표를 모두 모은다.
good_left_inds = ((nz[0] >= win_yl)&(nz[0] < win_yh)&(nz[1] >= win_xll)&(nz[1] < win_xlh)).nonzero()[0]
good_right_inds = ((nz[0] >= win_yl)&(nz[0] < win_yh)&(nz[1] >= win_xrl)&(nz[1] < win_xrh)).nonzero()[0]
left_lane_inds.append(good_left_inds)
right_lane_inds.append(good_right_inds)
# 구한 x좌표 리스트에서 흰색점이 5개 이상인 경우에 한해 x 좌표의 평균값을 구함. -> 이 값을 슬라이딩 윈도우의 중심점으로 사용
if len(good_left_inds) > minpix:
leftx_current = np.int(np.mean(nz[1][good_left_inds]))
if len(good_right_inds) > minpix:
rightx_current = np.int(np.mean(nz[1][good_right_inds]))
lx.append(leftx_current)
ly.append((win_yl + win_yh)/2)
rx.append(rightx_current)
ry.append((win_yl + win_yh)/2)
left_lane_inds = np.concatenate(left_lane_inds)
right_lane_inds = np.concatenate(right_lane_inds)
#left_fit = np.polyfit(nz[0][left_lane_inds], nz[1][left_lane_inds], 2)
#right_fit = np.polyfit(nz[0][right_lane_inds] , nz[1][right_lane_inds], 2)
# 슬라이딩 윈도우의 중심점(x좌표) 9개를 가지고 2차 함수를 만들어낸다.
lfit = np.polyfit(np.array(ly),np.array(lx),2)
rfit = np.polyfit(np.array(ry),np.array(rx),2)
# 왼쪽과 오른쪽 각각 파란색과 빨간색으로 색상 변경
out_img[nz[0][left_lane_inds], nz[1][left_lane_inds]] = [255, 0, 0]
out_img[nz[0][right_lane_inds] , nz[1][right_lane_inds]] = [0, 0, 255]
cv2.imshow("viewer", out_img)
return lfit, rfit
def draw_lane(image, warp_img, Minv, left_fit, right_fit):
global Width, Height
yMax = warp_img.shape[0]
ploty = np.linspace(0, yMax - 1, yMax)
color_warp = np.zeros_like(warp_img).astype(np.uint8)
left_fitx = left_fit[0]*ploty**2 + left_fit[1]*ploty + left_fit[2]
right_fitx = right_fit[0]*ploty**2 + right_fit[1]*ploty + right_fit[2]
# 이차함수 x = ay^2+by+c 이용해서 사다리꼴 이미지 외곽선 픽셀 좌표 계산
pts_left = np.array([np.transpose(np.vstack([left_fitx, ploty]))])
pts_right = np.array([np.flipud(np.transpose(np.vstack([right_fitx, ploty])))])
pts = np.hstack((pts_left, pts_right))
# 사다리꼴 이미지를 칼라로 그리고 거꾸로 원근변환해서 원본 이미지와 오버레이
color_warp = cv2.fillPoly(color_warp, np.int_([pts]), (0, 255, 0))
newwarp = cv2.warpPerspective(color_warp, Minv, (Width, Height))
return cv2.addWeighted(image, 1, newwarp, 0.3, 0)
def start():
global Width, Height, cap
_, frame = cap.read()
while not frame.size == (Width*Height*3):
_, frame = cap.read()
continue
print("start")
while cap.isOpened():
_, frame = cap.read()
image = calibrate_image(frame)
warp_img, M, Minv = warp_image(image, warp_src, warp_dist, (warp_img_w, warp_img_h))
left_fit, right_fit = warp_process_image(warp_img)
lane_img = draw_lane(image, warp_img, Minv, left_fit, right_fit)
cv2.imshow(window_title, lane_img)
cv2.waitKey(1)
if __name__ == '__main__':
start()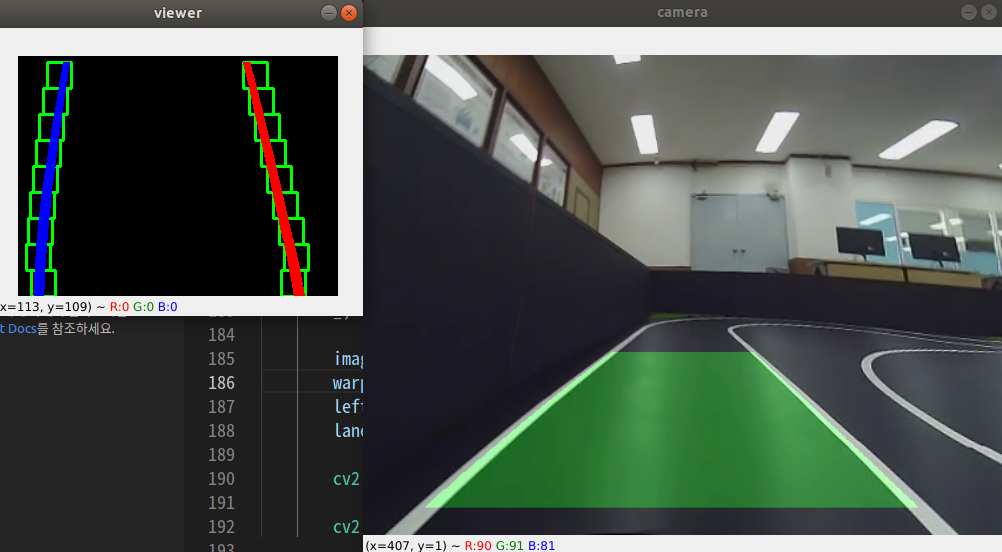
'ROS' 카테고리의 다른 글
| rosbag to image (0) | 2022.07.08 |
|---|---|
| 필터기반 조향각 제어 (0) | 2022.04.11 |
| 원근 변환과 슬라이딩 윈도우 (0) | 2022.04.10 |
| 와핑기법과 원근 변환 (0) | 2022.04.10 |
| 허프변환 기반 차선인식 (0) | 2022.04.10 |
Comments




